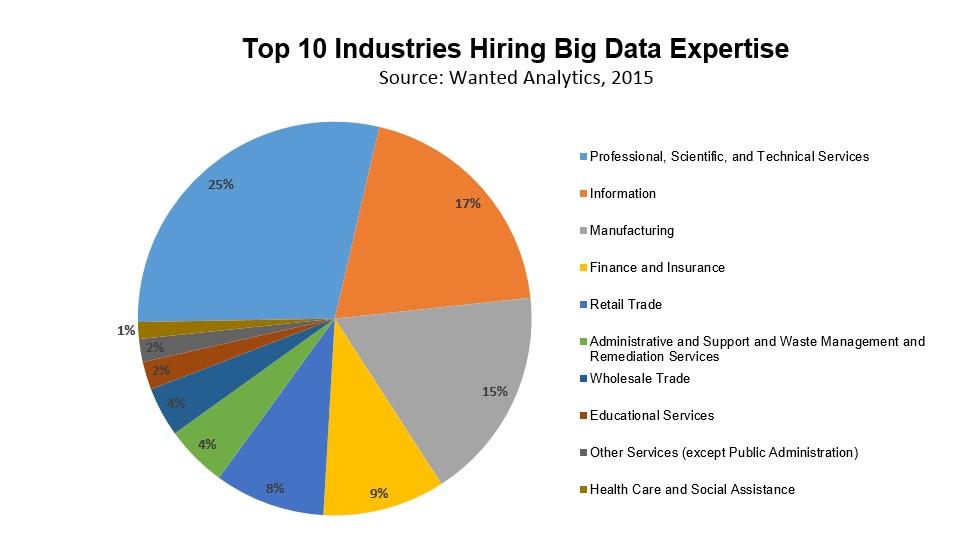
Big data is all about what organizations do with the massive amount of data collected on a day-to-day basis. The data gets collected at a faster rate in varied forms and large volumes. It is used by organizations and businesses to discover patterns and trends to understand human behavior. It helps to know how humans interact with technology, what products or information he consumes, and many more. These data are further used to make decisions for human benefit and profit. The analytics industry is doubling every 5 years. Big data analysts are trending. Almost every organization out there is recruiting data analysts to keep up with the humongous amount of data being generated every second and to wring actionable insights out of them. No doubt, the data analyst career path is something worth talking about. 'Is Big Data Analytics a good career?' If this is something that you have been asking about, then you will get your answers here. The data analytics career is unarguably one of the hottest options in the contemporary job market. But, what makes it dominate all other software jobs?
Title: Big Data Analyst
A big data analyst is someone who specializes in the analysis and presentation of large and complex data sets. This includes the identification, collection and analysis of big data for the purpose of improving decision making and gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
Must have technical skills required by the role
- Structured Query Language (SQL)
- Hadoop
- Microsoft Excel
- R or Python-Statistical Programming
- Data Visualization combined with any popular BI tool
- Presentation Skills
- Machine Learning
Soft skills required by the role
- Able to think logically and analytically in a problem-solving environment
- Imaginative, with skills in creative reasoning
- Able to work independently or as part of a team
- Good oral and written communication skills
- Able to accept responsibility
- Willing to continually update skills and knowledge
Typical Duties & Tasks of a Big Data Analyst
- Research how data is used and look at ways to improve use and efficiency
- Review and develop collection systems, processes and reporting
- Write reports describing findings, sometimes for publication
- Translate and extrapolate data
- Cross-reference and draw inferences from large, multiple data sets
- Present data and findings for a range of audiences.