The Internet of Things (IoT) has rapidly become one of the most familiar - and perhaps most hyped - expressions across business and technology. It is now used with data analytics software and artificial intelligence. These integrations help businesses improve processes, boost earnings and reduce overheads, especially in the challenging times that the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has created. IoT has paved the way for smart technologies just about anywhere. It is expected to rock different sectors, thanks to the increasing use of the cloud and the development of 5G. Smart appliances, security systems, phones, and cars are now commonplace. With its market size poised to be 1.6 trillion by the time we reach 2025, entrepreneurs and businesses from all corners are finding opportunities to enter the segment.
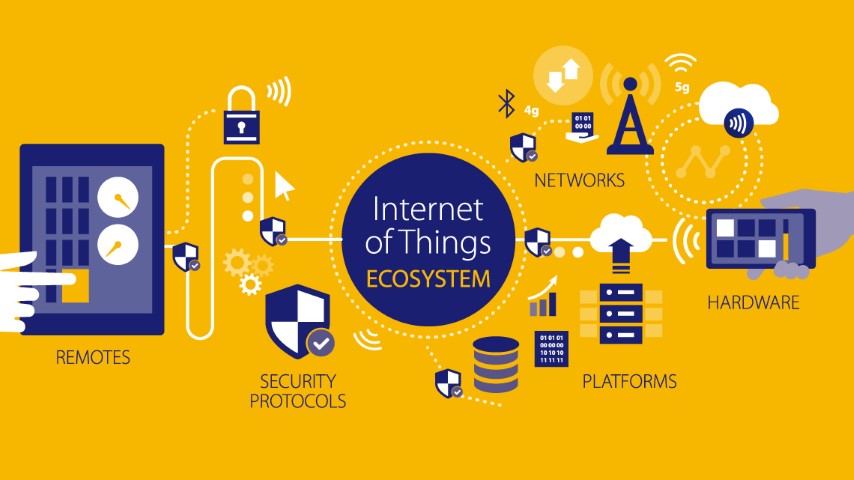
IoT ecosystem
IoT devices don't exist in a void. A lone sensor isn't really good for anything, nor is a bunch of them, for that matter, unless they are all connected to one another and to platforms that generate data for further use. This is what we call an Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem - a broad network of connected and interdependent devices and technologies that are applied by specialists towards a specific goal, such as the creation of a smart city.
Obviously, there are limitless applications to the IoT and therefore we can speak of endless coexisting IoT ecosystems. But if you boil what is happening in the ecosystem down to the bare essentials, you will come up with a simple schema: a device collects data and sends it across the network to a platform that aggregates the data for future use by the agent. And so we have the key components to an IoT ecosystem: devices, networks, platforms, and agents.
Sensors and actuators - sensors and actuators are at the centre of the entire IoT network. Sensors are connected to assets in the form of a physical micro appliance, embedded into an IoT device. These sensors are responsible for collecting and gathering data in order to send signals or commands to the actuator. The actuator then responds to the signal or command and "acts" or makes something happen based on this signal. As an example, your office may make use of a smart air conditioning system that is set to a specific temperature. Sensors are used to monitor any changes in temperature in the office environment. If a change is detected, they send a signal to the actuators, which will then automatically adjust the airflow.
Connectivity - this is largely referred to as the network layer and talks to how data is transferred and processed to ensure seamless communication between connected devices, sensors, the cloud, and actuators. For this to work efficiently, these elements need to be interconnected in order to understand the data and respond with the appropriate action. This is where IoT protocols and IoT gateways come in. IoT protocols provide a medium of transport for data collected from sensors. Data then goes through an IoT gateway that collects and translates the data being received via the protocols.
IoT Cloud - once the data has traveled through the IoT protocols and gateway, it moves to the cloud. The cloud is a high performance compute and storage ecosystem that is used for processing and data storage and brings all the different components of IoT together. In the cloud, data is filtered, managed, and stored. The data is then used to provide real-time analytics for fast decision making about what action should be taken in response to the data collected and signals received.
IoT analytics and data management - this is used to make sense of the large amounts of data being processed. IoT technology can compute all raw data, being collected and transported, into data analytics which provides actionable insights and real-time solutions that can be used for effective decision making.
Devices and interface - this is the visible component that an IoT user can use to control the system and set their preferences. This interaction is usually conducted on the device itself or remotely via smartphones, tablets, and laptops.